Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Takumi*; Nishi, Shusaku*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 3(12), p.4103 - 4112, 2023/12
Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Morishita, Kazuki; Marufuji, Takato; Ishikawa, Takashi; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Nakano, Tomoyuki
JAEA-Technology 2023-016, 41 Pages, 2023/09
This report summarizes the results of the stabilization treatments of post-experiment nuclear materials in Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) from August 2018 to March 2021. Based on the management standards for nuclear materials enacted after the contamination accident that occurred at PFRF on June 6, 2017, the post-experiment nuclear materials containing plutonium (Pu): samples mixed with organic substances that cause an increase in internal pressure due to radiolysis (including X-ray diffraction samples mixed with epoxy resin and plutonium powder which caused contamination accidents), carbides and nitrides samples which is reactive in air, and chloride samples which may cause corrosion of storage containers, were selected as targets of the stabilization. The samples containing organic materials, carbides and nitrides were heated in an air flow at 650  C and 950
C and 950  C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500
C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500  C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
Morishita, Kazuki; Sato, Takumi; Onishi, Takashi; Seki, Takayuki*; Sekine, Shinichi*; Okitsu, Yuichi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-024, 27 Pages, 2021/10
In the case of Plutonium (Pu)-bearing organic materials, organic materials are decomposed by alpha rays emitted mainly from Pu to generate hydrogen gas and other substances. Therefore, to safely store Pu-bearing organic materials for an extended period of time, organic materials must be eliminated. In addition, carbide and nitride fuels must be converted into oxides for safe storage in order to prevent the exothermal reaction of these fuels with oxygen/moisture in air. A survey of the literature on the stabilization treatment of Pu-bearing organic materials confirmed that organic materials can be decomposed and removed by heating at 950  C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950
C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950  C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950
C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950  C was lower than 2.1
C was lower than 2.1 10
10 Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950
Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950  C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
Terashima, Motoki; Endo, Takashi*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.380 - 387, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lin, P.*; Xu, C.*; Kaplan, D. I.*; Chen, H.*; Yeager, C. M.*; Xing, W.*; Sun, L.*; Schwehr, K. A.*; Yamazaki, Hideo*; Kokubu, Yoko; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 678, p.409 - 418, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.32(Environmental Sciences)Nagasaki sediments containing bomb-derived Pu provided a unique opportunity to explore the long term geochemical behavior of Pu. Through a combination of selective extractions and molecular characterization via electrospray ionization Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, we determined that 55  3% of the
3% of the 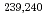 Pu was preferentially associated with more persistent organic matter compounds in Nagasaki sediments, particularly those natural organic matter (NOM) stabilized by Fe oxides. Other organic matter compounds served as a secondary sink of these
Pu was preferentially associated with more persistent organic matter compounds in Nagasaki sediments, particularly those natural organic matter (NOM) stabilized by Fe oxides. Other organic matter compounds served as a secondary sink of these 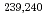 Pu (31
Pu (31  2% on average), and less than 20% of the
2% on average), and less than 20% of the 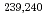 Pu was immobilized by inorganic mineral particles. While present long-term disposal and environmental remediation modeling assume that solubility limits and sorption to mineral surfaces control Pu subsurface mobility, our observations suggest that NOM undoubtedly plays an important role in sequestering Pu. Ignoring the role of NOM in controlling Pu fate and transport is not justified in most environmental systems.
Pu was immobilized by inorganic mineral particles. While present long-term disposal and environmental remediation modeling assume that solubility limits and sorption to mineral surfaces control Pu subsurface mobility, our observations suggest that NOM undoubtedly plays an important role in sequestering Pu. Ignoring the role of NOM in controlling Pu fate and transport is not justified in most environmental systems.
 Cs in forest surface environments; Application to a contaminated forest site near Fukushima and assessment of potential impacts of soil organic matter interactions
Cs in forest surface environments; Application to a contaminated forest site near Fukushima and assessment of potential impacts of soil organic matter interactionsOta, Masakazu; Nagai, Haruyasu; Koarashi, Jun
Science of the Total Environment, 551-552, p.590 - 604, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:72.19(Environmental Sciences)A model for  Cs transfer in forest was developed to assess behavior of Fukushima-derived
Cs transfer in forest was developed to assess behavior of Fukushima-derived  Cs. The model simulation well reproduced observed 3 year migration of
Cs. The model simulation well reproduced observed 3 year migration of  Cs in organic layer and mineral soil. Long-term predictions indicated that more than 90% of the deposited
Cs in organic layer and mineral soil. Long-term predictions indicated that more than 90% of the deposited  Cs remains in the top 5 cm soil till 30 years, suggesting that forest acts as a long-term reservoir of
Cs remains in the top 5 cm soil till 30 years, suggesting that forest acts as a long-term reservoir of  Cs with limited loss via groundwater pathway. Impacts of soil organic matter (SOM) on
Cs with limited loss via groundwater pathway. Impacts of soil organic matter (SOM) on  Cs dynamics were investigated by modifying parameters of
Cs dynamics were investigated by modifying parameters of  Cs turnover. The results showed that SOM-induced reduction of
Cs turnover. The results showed that SOM-induced reduction of  Cs adsorption, slower fixation of
Cs adsorption, slower fixation of  Cs by clay and enhanced mobilization of the fixed
Cs by clay and enhanced mobilization of the fixed  Cs elevate soil-to-plant transfer of
Cs elevate soil-to-plant transfer of  Cs by increasing fraction of dissolved
Cs by increasing fraction of dissolved  Cs. A substantial proportion (27%
Cs. A substantial proportion (27%  73%) of
73%) of  Cs in these soils was delivered to horizons deeper than 5 cm decades later. These results suggested that SOM significantly influences behavior of
Cs in these soils was delivered to horizons deeper than 5 cm decades later. These results suggested that SOM significantly influences behavior of  Cs over long-term.
Cs over long-term.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Hashimoto, Shoji; Kojima, Takuji
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 75(10), p.2177 - 2183, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.18(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Matsunaga, Takeshi; Nagao, Seiya*
Sui Kankyo Gakkai-Shi, 25(4), p.193 - 197, 2002/04
no abstracts in English
Matsunaga, Takeshi; Nagao, Seiya*; Takeda, Seiji; Ueno, Takashi; Amano, Hikaru
Dai-43-Kai Kankyo Hoshano Chosa Kenkyu Seika Rombun Shorokushu (Heisei-12-Nendo), p.49 - 50, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Arai, Hidehiko; Hashimoto, Shoji
Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 34(10), p.1300 - 1308, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.13(Engineering, Chemical)The continuous gas monitoring system using the mass filter (CGM-MS) was developed for the measurement of gaseous substances in air under atmospheric pressure. A capillary tube introduces the gases under atmospheric pressure into a mass filter installed in a vacuum chamber. The CGM-MS detected gaseous substances, such as sulfur dioxide, benzene and chlorobenzene, with detectable sensitivity of 0.7-1 ppmv. The monitoring system was also applied for the analysis of the products formed in electron beam irradiation of trichloroethylene (TCE) and air mixture. Dichloroacetyl chloride, carbonyl chloride (COCl ), and chlorine (Cl
), and chlorine (Cl ) were quantitatively analyzed. Trichloroethylene and the products were oxidized and completely converted into carbon dioxide, Cl
) were quantitatively analyzed. Trichloroethylene and the products were oxidized and completely converted into carbon dioxide, Cl , and hydrochloric acid at 15 kGy. Carbonyl chloride is dissolved in an alkaline solution to be automatically oxidized into CO
, and hydrochloric acid at 15 kGy. Carbonyl chloride is dissolved in an alkaline solution to be automatically oxidized into CO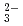 and Cl
and Cl . The combination of the irradiation and the dissolution of the irradiated gas decreased to 7 from 15 kGy for the complete oxidation of TCE and the products.
. The combination of the irradiation and the dissolution of the irradiated gas decreased to 7 from 15 kGy for the complete oxidation of TCE and the products.
Sun, Y.*; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Chmielewski, A. G.*; Hashimoto, Shoji; Zimek, Z.*; Bulka, S.*; Ostapczuk, A.*; Nichipor, H.*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 62(4), p.353 - 360, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:81.38(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Hirota, Koichi; Hashimoto, Shoji
Proceedings of 5th International Symposium & Exhibition on Environmental Contamination in Central & Eastern Europe (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2001/09
no abstracts in English
 P) radicals, thermal electrons, and O
P) radicals, thermal electrons, and O in electron beam irradiation of 1,2-dichloroethylenes and air mixtures
in electron beam irradiation of 1,2-dichloroethylenes and air mixturesHakoda, Teruyuki; Zhang, G.*; Hashimoto, Shoji
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 62(2-3), p.243 - 252, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:66.91(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Fukumoto, Masahiro; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*
JNC TN8400 2001-017, 355 Pages, 2001/03
The alkali hydrolysis experiments which seem to be important from the view point of the alteration mechanism using the following seven organic materials was performed as a part of the evaluation of the influence on the disposal of the organic materials contained in the TRU wastes. As a result of the alkali hydrolysis experiments (90 C and 91d), each organic materials became those of lower molecular weight. The degradation products were able to be detected in the solution. The organic materials seem to be degraded to the organic matters which were confirmed in this study in a long term of disposal. The degradation products were shown below. Therefore, the evaluation of the influence on the migration of radionuclides by degradation products becomes important in the future. (1)Cement additives of Naphthalenesulfonic acid and Ligninsulfonic acid (
C and 91d), each organic materials became those of lower molecular weight. The degradation products were able to be detected in the solution. The organic materials seem to be degraded to the organic matters which were confirmed in this study in a long term of disposal. The degradation products were shown below. Therefore, the evaluation of the influence on the migration of radionuclides by degradation products becomes important in the future. (1)Cement additives of Naphthalenesulfonic acid and Ligninsulfonic acid ( Naphthalenedisulfonic acid etc.) (2)Cement additives of polycarboxylic acid (
Naphthalenedisulfonic acid etc.) (2)Cement additives of polycarboxylic acid ( Oligomer of distal methoxypoly ethylene glycol.) (3)Ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid disodium salt (
Oligomer of distal methoxypoly ethylene glycol.) (3)Ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid disodium salt ( Acetic acid desorped and cyclized organic matters from EDTA.) (4)Tributyl phosphate (
Acetic acid desorped and cyclized organic matters from EDTA.) (4)Tributyl phosphate ( Dibutyl phthalate, n-butanol) (5)Poly vinyl acetate (
Dibutyl phthalate, n-butanol) (5)Poly vinyl acetate ( Acetic acid) (6)Nylon66 (
Acetic acid) (6)Nylon66 ( Adipic acid, Hexamethylenediamine) (7)Cured epoxy resin (
Adipic acid, Hexamethylenediamine) (7)Cured epoxy resin ( Glycerol poly glycidyl ether, Carboxylic acid)
Glycerol poly glycidyl ether, Carboxylic acid)
Ogawa, Hiromichi; Nagao, Seiya; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki; Munakata, Masahiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; Nakayama, Shinichi; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo; Kumata, Masahiro; et al.
JAERI-Research 2000-052, 101 Pages, 2001/01
no abstracts in English
Fukumoto, Masahiro; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Kagawa, Akio; Kawamura, Kazuhiro
JNC TN8400 2001-002, 23 Pages, 2000/12
The soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt ( ray) were confirmed as a part of influence of the bituminized waste degradation in the TRU waste repository. Especially, the influence of the nitrate was focused on. As a result, the concentration of the soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt (10MGy,
ray) were confirmed as a part of influence of the bituminized waste degradation in the TRU waste repository. Especially, the influence of the nitrate was focused on. As a result, the concentration of the soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt (10MGy,  ray which is correspond to absorbed dose of asphalt for 1,000,000 years) were lower (each formic acid : about 50mg/dm
ray which is correspond to absorbed dose of asphalt for 1,000,000 years) were lower (each formic acid : about 50mg/dm , acetic acid : about 30mg/dm
, acetic acid : about 30mg/dm and oxalic acid : about 2mg/dm
and oxalic acid : about 2mg/dm ) than that of the formic acid, the acetic acid and the oxalic acid which Valcke et al. had shown (the influence of the organic at the solubility examination which uses Pu and Am). Moreover, the change in the concentration of TOC and the soluble organic compounds (formic acid, acetic acid and oxalic acid) is little under the existence of nitrate ion. That is, the formic acid and acetic acid which can be organic ligands were generated little by oxidative decomposition of asphalt in the process that nitrate ion becomes nitrite ion by radiation. The influence of the soluble organic compounds by the radiological degradation of the asphalt (
) than that of the formic acid, the acetic acid and the oxalic acid which Valcke et al. had shown (the influence of the organic at the solubility examination which uses Pu and Am). Moreover, the change in the concentration of TOC and the soluble organic compounds (formic acid, acetic acid and oxalic acid) is little under the existence of nitrate ion. That is, the formic acid and acetic acid which can be organic ligands were generated little by oxidative decomposition of asphalt in the process that nitrate ion becomes nitrite ion by radiation. The influence of the soluble organic compounds by the radiological degradation of the asphalt ( ray) on adsorption and solubility by the complexation of radionuclides in the performance assessment can be limited.
ray) on adsorption and solubility by the complexation of radionuclides in the performance assessment can be limited.
Hashimoto, Shoji; Arai, Hidehiko
Denki Gakkai Gijutsu Hokoku, (810), p.46 - 50, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2000-010, 27 Pages, 2000/07
In the geological disposal system of the radioactive wastes, gas generation by microorganism could be significant for the assessment of this system, because organic material included in groundwater, buffer material and wastes might serve as carbon sources for microorganisms. In this study, gas generation tests using microorganisms were carried out under anaerobic condition. The amount of methane and carbon dioxide that were generated by activity of Methane Producing Bacteria (MPB) were measured with humic acid, acetic acid and cellulose as carbon sources. The results showed that methane was not generated from humic acid by activity of MPB. However, in the case of using acetic acid and cellulose, methane was generated, but at high pH condition (pH=10), the amount of generated methane was lower than at low pH (pH=7). It was not clear whether the pH would affect the amount of generated carbon dioxide.
; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Kagawa, Akio;
JNC TN8400 2000-017, 30 Pages, 2000/03
The influence of the cement additives on the distribution coefficients of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite was confirmed. The adsorption experiment of americium-241 to Ca-bentonite with cement additives was performed by the batch method, as a part of the influence evaluation of the organic in the research of TRU waste disposal. As a result, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite was over 1.2E+3m /kg in the condition of the absence of cement additives. In the case of low concentration (0.3g/kg) of the naphthalenesulfonic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 5.2E+2m
/kg in the condition of the absence of cement additives. In the case of low concentration (0.3g/kg) of the naphthalenesulfonic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 5.2E+2m kg. And, in the case of high concentration (30g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficients was 2.0E-1m
kg. And, in the case of high concentration (30g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficients was 2.0E-1m /kg. On the other hand in the case of flow concentration (0.5g/kg) of the polycarboxylic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficients was over 1.3E+3m
/kg. On the other hand in the case of flow concentration (0.5g/kg) of the polycarboxylic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficients was over 1.3E+3m /kg. And, in the case of high concentration (50g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 1.8E-1m
/kg. And, in the case of high concentration (50g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 1.8E-1m /kg. Here, selected cement additives concentrations were based on a standard concentration of 10g/kg when the ratio of water:cement is about one. From these results, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite decreases according cement additive concentration. The distribution coefficients were similar on different kinds of cement additives. The cement additives concentration influences the distribution coefficient. The distribution coefficient was small in the case of high concentration of the cement additives. That is, it is thought that the cement additives have small influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of low concentration, though the cement additives have influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of high concentration.
/kg. Here, selected cement additives concentrations were based on a standard concentration of 10g/kg when the ratio of water:cement is about one. From these results, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite decreases according cement additive concentration. The distribution coefficients were similar on different kinds of cement additives. The cement additives concentration influences the distribution coefficient. The distribution coefficient was small in the case of high concentration of the cement additives. That is, it is thought that the cement additives have small influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of low concentration, though the cement additives have influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of high concentration.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Zhang, G.; Hashimoto, Shoji
JAERI-Conf 2000-001, p.211 - 214, 2000/03
no abstracts in English